Optimizing Networks with SRv6 Flex Algorithm Slicing
March 24, 2025 | Pavan Chaudhari
Segment Routing over IPv6 (SRv6) has fundamentally transformed modern networking by simplifying the transport layer and introducing unparalleled programmability. Among its significant advancements, the Flex Algorithm (Flex-Algo) stands out as a groundbreaking feature, offering enhanced flexibility for traffic engineering and network optimization. Flex-Algo, when integrated with SRv6, provides a powerful mechanism to create constraint-based, customized routing topologies that meet diverse service requirements while maximizing network efficiency.
Key Features and Benefits of Flex Algorithm in SRv6:
- Customized Routing Topologies:
Flex-Algo extends traditional Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) such as OSPF and IS-IS by enabling operators to define custom routing constraints. These constraints may include parameters like latency, bandwidth, link/node avoidance, or any other metric critical to service-level agreements (SLAs). Flex-Algo defines unique topologies tailored to these constraints, enabling traffic to follow paths that align with the desired service characteristics. - Network Slicing with Flex-Algo and SRv6:
Flex-Algo, combined with SRv6, enables SRv6 Network Slicing, a capability that allows operators to partition a physical network into multiple virtualized and isolated slices. Each slice can be tailored to specific use cases, such as low-latency services, high-bandwidth applications, or mission-critical operations. This is achieved by associating each slice with a unique Flex-Algo ID and mapping it to specific SRv6 Segment Identifiers (SIDs) or policies. For instance:- Low-latency slices prioritize delay-sensitive paths, such as those needed for 5G applications or real-time IoT communication.
- High-bandwidth slices focus on paths with maximum capacity to accommodate data-intensive applications like video streaming.
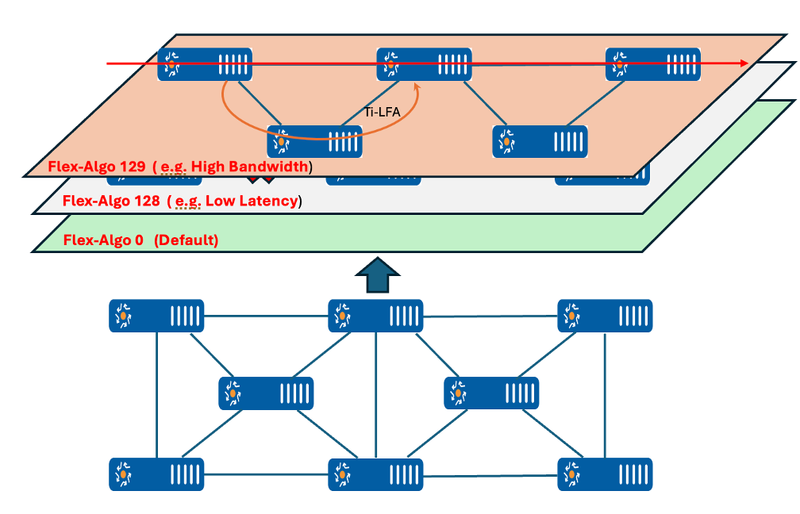
Figure 1 – Network Slicing Using Flex Algo
- Efficient Traffic Engineering:
SRv6 uses IPv6-based Segment Identifiers (SIDs) to encode path information directly into packet headers. When combined with Flex-Algo, the routing becomes more dynamic and efficient. Flex-Algo ensures that traffic adheres to the precomputed, constraint-based paths defined for each slice, optimizing resource utilization and meeting service-specific requirements. - Reliability Through TI-LFA:
Flex-Algo integrates seamlessly with Topology Independent Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA), a mechanism for fast rerouting in case of network failures. Importantly, TI-LFA ensures that backup paths for any particular Flex-Algo remain within the same slice. This guarantees slice isolation and reliability, even during node or link failures, making it particularly beneficial for critical applications. - Scalability with a Stateless Core:
By leveraging the principles of segment routing, Flex-Algo ensures that the core of the network remains stateless. This simplifies network operations while allowing fine-grained routing granularity at the edges. Operators can adapt the network to diverse and evolving service demands without overburdening the core infrastructure. - Support for Emerging Applications:
The combination of SRv6 and Flex-Algo is particularly suited for next-generation applications, such as:- 5G: Enables ultra-reliable, low-latency communication (URLLC), enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), and massive IoT services by providing dedicated network slices.
- IoT: Offers optimized routing for delay-sensitive or resource-constrained IoT devices.
- Enterprise Services: Delivers isolated and SLA-compliant slices for critical business applications.
How Flex-Algo Works in SRv6:
To send traffic through a desired path that is not the IGP shortest path, we have two options: configuring an explicit path or using Flex-Algo. For an explicit path, multiple SIDs need to be pushed onto the packet to direct traffic through the desired path. In contrast, with Flex-Algo, the router runs SPF for the specific Flex-Algo by excluding unwanted links and forwards traffic over the constrained path by simply pushing the destination SID, as explained in the table below.

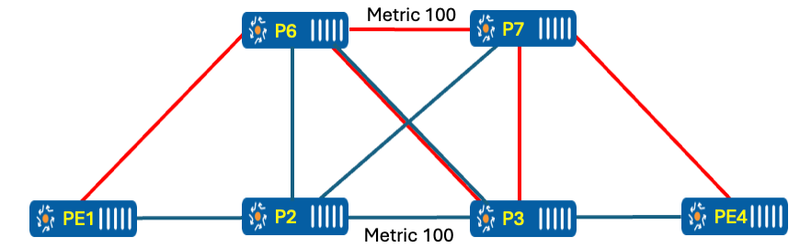
Figure 2 – Lab Topology
According to RFC 8402: Segment Routing Architecture, Flex-Algos offer operators the flexibility to define custom routing paths based on network performance metrics.
By default, ArcOS supports below algorithms,
- Flex-Algo 0 (Shortest Path First - SPF) - Flex-Algo 0 calculates the shortest path using IGP metrics
- Flex-Algo 1 (Strict-SPF) - Flex-Algo 1 enforces strict adherence to this path without deviations.
- Flex-Algos 128–255 - Additionally, operators can create custom algorithms (Flex-Algos 128–255) to optimize paths for metrics like delay, bandwidth, or specific link constraints, using mechanisms such as include/exclude link colors and TE metrics , link delay or High Bandwidth.
Each IGP node is configured with an SRv6 locator value for Flex-Algos, enabling the computation of shortest paths based on defined objectives while reducing SID complexity through segment aggregation.
The implementation of Flex-Algos ensures consistent path computation across nodes by advertising Flex-Algo definitions through Router Capability TLVs (ISIS) or Router Information LSAs (OSPF). This consistency prevents routing loops and guarantees optimal path selection. In advanced use cases like dual-plane disjoint paths, Flex-Algos provide resiliency by delivering strict disjoint paths for critical traffic, even under failure conditions, while leveraging ECMP for other traffic streams. With ArcOS, headend nodes support SRv6 traffic steering by adding Segment Routing Headers (SRH), ensuring efficient routing via SR-TE policies mapped to endpoint attributes and SID lists. Flex-Algos simplify operational complexity and enable scalable, resilient, and efficient traffic management.
When computing paths for a given Flex-Algo(K), a node first removes all non-participating nodes and prunes resources that do not meet the constraints of Flex-Algo(K), resulting in a refined topology called Topo(K). The nodes then leverage Dijkstra’s algorithm to compute the shortest path graph on this topology, optimizing the specified metric, such as IGP, TE, or link delay. Equal-Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) is supported, allowing traffic to be load-balanced across multiple paths with equal cost for the algorithm. For enhanced resiliency, TI-LFA (Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternate) provisions backup paths for the SRv6 Prefix-SIDs of each Flex-Algo(K). These backup paths are computed based on the same constraints and optimization metrics as the primary paths, ensuring continuity during failure scenarios.
As depicted in the diagram below, the network can be sliced according to bandwidth, delay, or link coloring based on the network requirements. In the diagram, slicing is illustrated based on link coloring: Flex-Algo 128 corresponds to RED-colored links, Flex-Algo 129 corresponds to Blue-colored links, with the default Flex-Algo 0 applying to the entire topology. ISIS carries FAD information in the TLV ROUTER_CAPABILITY and its sub-TLVs, including ROUTER_CAPABILITY_SRV6_CAPABILITY.
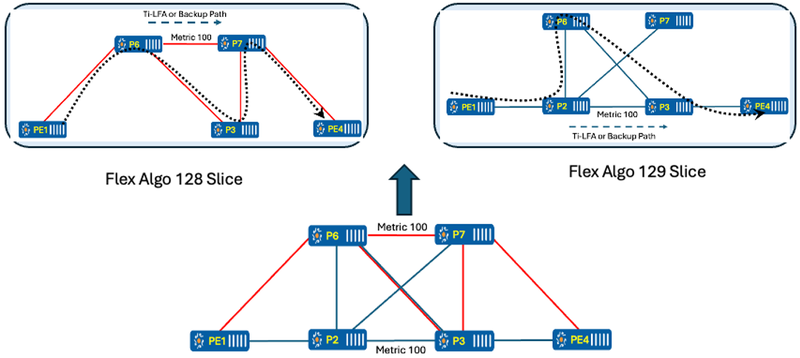
Figure 3 Flex-Algo 128 and 129 Slices
On Demand Next-hop Configuration (ODN)
At this stage, the network has been sliced using Flex-Algo, and traffic must be directed along the desired path based on specific requirements. In ArcOS implementation, this involves two steps: first, setting the extended color community, and second, configuring the SR-policy with the corresponding color on the ingress router. When remote prefixes 192.168.100.100 and 192.168.200.200 reach PE-01 with their respective color extended communities, the corresponding SR-policies are activated, ensuring traffic is forwarded over the appropriate Flex-Algo paths.
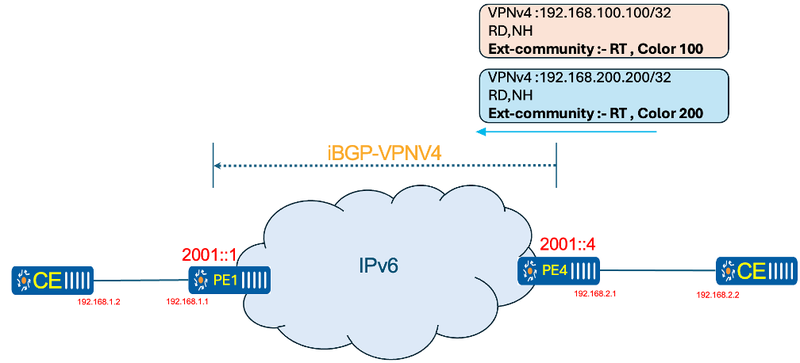
Figure 4 Extended community setting at egress PE
Use Cases
- Low-Latency Routing: designed for low-latency applications, such as autonomous vehicles or augmented reality. Flex-Algo ensures that traffic on this slice follows paths with the least delay.
- Bandwidth Optimization: optimized for high-bandwidth services like video streaming or file transfers, where Flex-Algo routes traffic through high-capacity links.
- Avoiding Congestion: Dynamically reroute traffic to avoid congested or degraded network paths.
- Redundancy and Resiliency: supports mission-critical operations, such as emergency response systems, with TI-LFA providing robust protection against failures within the slice.
Future Prospects
- AI and ML Integration: Combining Flex Algorithm with AI/ML for predictive and adaptive routing.
- IoT and 5G Optimization: Enhancing performance for IoT and 5G networks through precise routing.
- Cloud-Native Networking: Flex Algorithm will play a vital role in optimizing cloud and multi-cloud environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SRv6 Flex Algorithm represents a significant leap forward in Traffic Engineering and network optimization. By empowering network operators with the ability to define custom routing policies and slice the network based on requirements, it ensures the network infrastructure adapts to evolving application demands, providing high performance and operational efficiency.
Since the beginnings of Segment Routing, an SRv6 SID is associated with a prefix and an algorithm. Most often, the SRv6 SID algorithm is the default one (zero).
With algorithm zero, the IGP SRv6 SID is steered via the shortest IGP path to its associated prefix (i.e., the shortest path as computed by ISIS and OSPF).
Algorithms 0 to 127 are standardized by the IETF. Algorithms 128 to 255 are customized by the operator and are called SR IGP Flexible Algorithms (Flex-Algo for short). For example, one operator may define Flex-Algo(128) to minimize delay, while another operator defines Flex-Algo(128) to minimize the IGP metric and avoid the TE-affinity RED. Yet another operator could define Flex-Algo(128) as a minimization of the TE metric and avoidance of SRLG 20.Any node participating in a Flex-Algo advertises its support for this Flex-Algo.
FlexAlgo
NETWORKING
SRV6
Categories
5G
ACE
AI
ArcEdge
ArcIQ
ARCOS
ARRCUS
CLOUD
datacenters
edge
FlexAlgo
hybrid
Internet
INVESTING
IPV4
IPV6
MCN
ML
multicloud
Multicloud
MUP
NETWORKING
NETWORKING INDUSTRY
Routing
SRV6
uSID