YANG Module Versioning and Semver: Importance and impact on Internet-Draft Authors
November 19, 2025 | Mahesh Jethanandani
YANG enables comprehensive network automation by providing a standardized way to model the configuration and state data of network elements. The NETMOD Working Group (WG) is getting ready to publish the long-awaited updated versioning scheme for YANG modules published by IETF. These changes will impact current authors of Internet-Drafts (I-Ds) that contain a YANG module.
The NETwork MODeling (NETMOD) WG is responsible for the development and maintenance of the Yet Another Next Generation (YANG) language. The YANG language is a data modeling language used to define how the data is sent over network management protocols such as the NETCONF and RESTCONF. The current YANG [RFC7950] versioning mechanism follows a strict backward compatible model with a format that is represented as a date in the form of YYYY-MM-DD. Industry deployment of YANG modules has revealed that a strict adherence to the backward compatibility requirement is impeding the evolution of the language and the solutions it offers.
The Change
The NETMOD WG has submitted to the Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG) a trio of documents for publication as RFCs—draft-ietf-netmod-yang-module-versioning, draft-ietf-netmod-yang-semver, and draft-ietf-netmod-yang-module-filename—that will update how YANG modules published by IETF will be versioned. The documents have to complete IETF Last Call and have to be reviewed by the IESG and, as such, are subject to change. However, because of the significant implications of the changes, it is important for I-D authors to be aware of them now.
Once approved for publication, the changes proposed by these documents will impact authors who want to publish YANG modules in the IETF, and WGs that progress these changes. Authors of I-Ds that contain YANG modules use tools to validate or extract the YANG module from the I-D. These will be updated to support this new capability. These changes will come into force when the three I-Ds are approved for publication by the IESG.
The first document, “Updated YANG Module Revision Handling” (draft-ietf-netmod-yang-module-versioning) refines the RFC 7950 module update rules. It specifies a new YANG module update procedure that can document, via a new YANG extension, when non-backwards-compatible changes have occurred during the evolution of a YANG module.
The second document, “YANG Semantic Versioning” (draft-ietf-netmod-yang-semver) specifies a YANG extension along with guidelines for applying an extended set of semantic versioning rules to revisions of YANG artifacts (e.g., modules and packages).
Finally, “YANG Module File Name Convention” (draft-ietf-netmod-yang-module-filename) defines a YANG module file name convention. The convention extends the current YANG module file name using revision‑date, with the YANG semantic version extension.
Typically either revision-date or ysv:version is expected to be used for a YANG module, i.e. only one file should exist. But when migrating from one schema to another, files with both versioning schemes may exist until the migration is complete.
Why these changes are being made
This set of documents recognizes the need to sometimes allow YANG modules to evolve with Non-Backwards-Compatible (non-backwards-compatible) changes, which can cause breakage to clients and when importing YANG modules. Allowing for these non-backwards-compatible changes do sometimes occur—e.g., for bugfixes—requires mechanisms to report when these changes occur, and to manage their effect on clients and the broader YANG ecosystem.
These changes are the foundation for other work in progress in the NETMOD WG. Current I-Ds include “YANG Schema Comparison” draft-ietf-netmod-yang-schema-comparison, YANG Packages draft-ietf-netmod-yang-packages, and YANG Schema Selection draft-ietf-netmod-yang-ver-selection. New contributors, i.e., input, to this on-going work are welcome and should be made to the NETMOD WG email list.
Here are some of the changes that one can expect:
- A new rev:non-backwards-compatible statement will need to be added to YANG modules published by IETF, if the YANG module is non-backwards compatible compared to the previously published version. The statement is defined in draft-ietf-netmod-yang-module-versioning
- A new version statement will need to be added to YANG modules published by IETF. An example of the version statement is as follows where ‘ysv’ refers to the prefix for the module ‘ietf-yang-semver’ defined in draft-ietf-netmod-yang-server.
revision 2017-08-30 {
description "Add 'wibble' leaf";
ysv:version 2.1.0;
}
revision 2017-07-30 {
description "Rename 'baz' to 'bar'";
ysv:version 2.0.0;
rev:non-backwards-compatible;
}
revision 2017-04-03 {
description "Add new functionality, leaf 'foo'";
ysv:version 1.1.0;
}
revision 2017-02-07 {
description "Initial version.";
ysv:version 1.0.0;
}
When the YANG modules are extracted from an I-D, the tool will create two files. The first filename has the format that is used today. An example is:
ietf-interfaces@2018-02-20.yang
In addition, a second filename will be created that will follow the YANG Semver format. An example of that filename would be:
ietf-interfaces#1.0.0.yang
- The Datatracker tools will be updated to check for the presence of the ysv:version statement in the draft. While new modules will add this version statement, existing modules that undergo a bis, or a change, should retroactively assign version statements to older versions statements in the updated module.
The YANG semantic version is expressed as a string of the form: 'X.Y.Z', where:
- The ‘X’, which is a MAJOR indicates changes that are non-backwards-compatible to versions with a lower MAJOR version number.
- The 'Y' which is a MINOR version indicates changes that are Backwards-Compatible (non-backwards-compatible) to versions with the same MAJOR version number, but a lower MINOR version number and no _COMPAT modifier.
- The 'Z' is the PATCH version indicates an editorial change to the YANG artifact.
- There is also an optional _COMPAT suffix (X.Y.Z_COMPAT, e.g. ysv:version 1.2.1_non_compatible) but the IETF is not expected to make use of the _COMPAT modifiers (they are more for branched module development).
The best way to understand this versioning scheme and the limited branching it supports is with a tree visual depicting a YANG module changing over time::
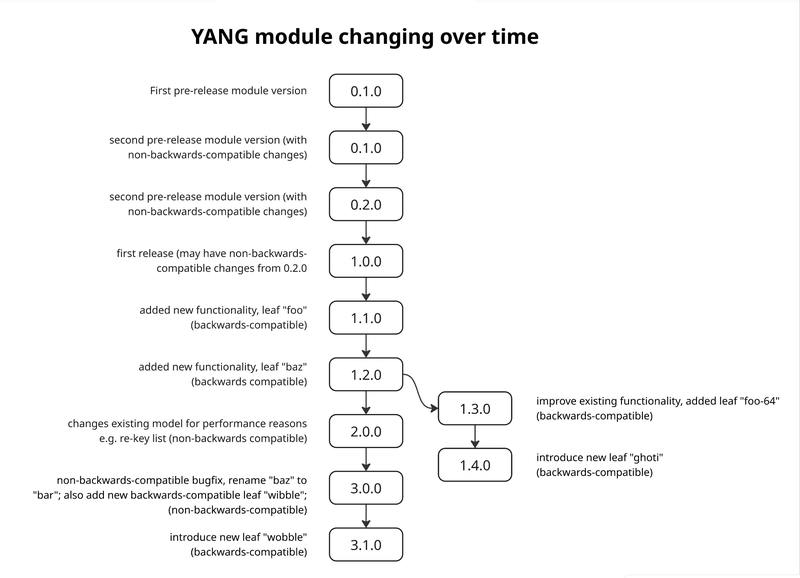
Example tree visual depicting a YANG module changing over time
Read further on IETF website
AI
YANG
Categories
5G
ACE
AI
ArcEdge
ArcIQ
ARCOS
ARRCUS
CLOUD
datacenters
edge
FlexAlgo
hybrid
Internet
INVESTING
IPV4
IPV6
MCN
ML
multicloud
Multicloud
MUP
NETWORKING
NETWORKING INDUSTRY
Routing
SRV6
uSID